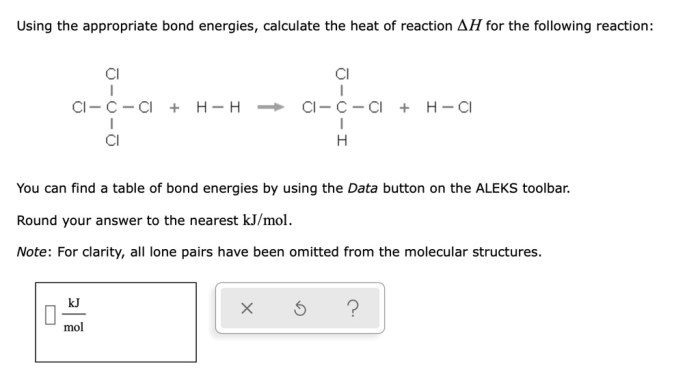
Conjugate acid base pairs worksheet – Delve into the fascinating world of conjugate acid-base pairs with our comprehensive worksheet, designed to unravel the intricacies of this fundamental chemical concept. Understand the relationship between acids and bases and their conjugate counterparts, empowering you to navigate the complexities of chemical reactions.
Throughout this worksheet, you’ll explore the properties of conjugate acid-base pairs, their impact on pH, and their diverse applications in everyday life, industry, and research.
Introduction: Conjugate Acid Base Pairs Worksheet
In chemistry, conjugate acid-base pairs are pairs of substances that can interconvert by the transfer of a proton (H+ ion).
When an acid donates a proton, it becomes its conjugate base. Conversely, when a base accepts a proton, it becomes its conjugate acid.
Relationship between Conjugate Acids and Bases, Conjugate acid base pairs worksheet
The relationship between conjugate acids and bases is reciprocal. The conjugate acid of a base is the acid that is formed when the base accepts a proton. Conversely, the conjugate base of an acid is the base that is formed when the acid donates a proton.
The strength of an acid is inversely related to the strength of its conjugate base. A strong acid has a weak conjugate base, and a weak acid has a strong conjugate base.
Identifying Conjugate Acid-Base Pairs
Conjugate acid-base pairs are two species that differ by a single proton (H +). The acid is the proton donor, and the base is the proton acceptor.
To identify conjugate acid-base pairs, we can use the following method:
- Start with an acid (HA).
- Remove a proton (H+) from the acid to form the conjugate base (A –).
- The conjugate acid of A –is HA.
For example, the conjugate acid-base pair for water (H 2O) is:
- Acid: H 3O +
- Base: OH –
Here is a table with more examples of conjugate acid-base pairs:
| Acid | Base |
|---|---|
| HCl | Cl– |
| H2SO4 | HSO4– |
| HNO3 | NO3– |
Properties of Conjugate Acid-Base Pairs
Conjugate acid-base pairs exhibit unique properties that influence the chemical behavior of solutions. These properties include:
- Conjugate Acid Strength:The strength of a conjugate acid is inversely proportional to the strength of its conjugate base. A strong acid will have a weak conjugate base, and vice versa.
- Conjugate Base Strength:The strength of a conjugate base is directly proportional to the strength of its conjugate acid. A strong base will have a weak conjugate acid, and vice versa.
- pH Effect:Conjugate acid-base pairs can significantly affect the pH of a solution. A strong acid will lower the pH, while a strong base will raise the pH.
pH Effect of Conjugate Acid-Base Pairs
The pH of a solution is a measure of its acidity or basicity. It is determined by the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) in the solution. Conjugate acid-base pairs can alter the pH of a solution by releasing or consuming H+ ions.*
-*Strong Acids
Strong acids release a large number of H+ ions into solution, lowering the pH and making the solution more acidic.
-
-*Weak Acids
Weak acids release a small number of H+ ions into solution, having a less pronounced effect on the pH.
-*Strong Bases
Strong bases remove H+ ions from solution, raising the pH and making the solution more basic.
-*Weak Bases
Weak bases remove a small number of H+ ions from solution, having a less pronounced effect on the pH.
Understanding the properties of conjugate acid-base pairs is crucial for predicting and controlling the pH of solutions in various chemical and biological systems.
Applications of Conjugate Acid-Base Pairs
Conjugate acid-base pairs have a wide range of applications in everyday life, industry, and research. Their unique properties make them essential for various chemical processes and biological functions.
In everyday life, conjugate acid-base pairs are commonly used in:
- Food preservation: Citric acid and its conjugate base, citrate, are used as preservatives in canned foods and beverages to prevent spoilage.
- pH regulation: Buffers, which contain a weak acid and its conjugate base, are used to maintain a stable pH in solutions, such as in blood and chemical reactions.
- Medicine: Aspirin, a pain reliever, is a weak acid that forms a conjugate base in the body, helping to reduce inflammation.
Industry and Research
In industry and research, conjugate acid-base pairs are used in:
- Chemical synthesis: Acids and bases are used as catalysts and reagents in various chemical reactions to produce a wide range of products.
- Electrochemistry: Batteries and fuel cells rely on the reactions of conjugate acid-base pairs to generate electricity.
- Environmental monitoring: Acid rain, caused by the presence of conjugate acid-base pairs in the atmosphere, is monitored to assess environmental health.
- Biochemistry: Conjugate acid-base pairs play a crucial role in biological processes, such as enzyme catalysis, protein folding, and DNA replication.
General Inquiries
What are conjugate acid-base pairs?
Conjugate acid-base pairs are two species that differ by the transfer of a single proton (H+ ion).
How do I identify conjugate acid-base pairs?
To identify conjugate acid-base pairs, look for species that differ by a proton and have opposite charges.
What is the relationship between the strength of an acid and its conjugate base?
Strong acids have weak conjugate bases, and vice versa.