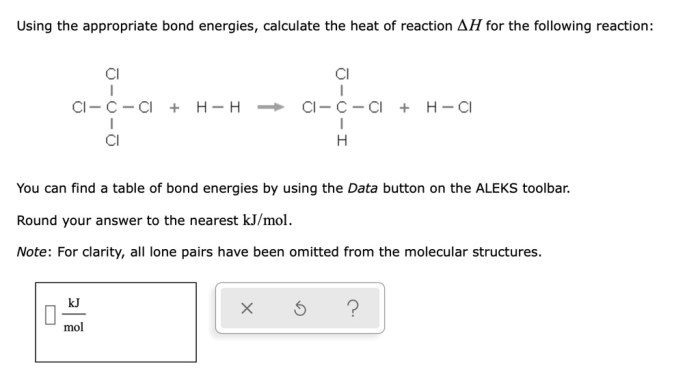
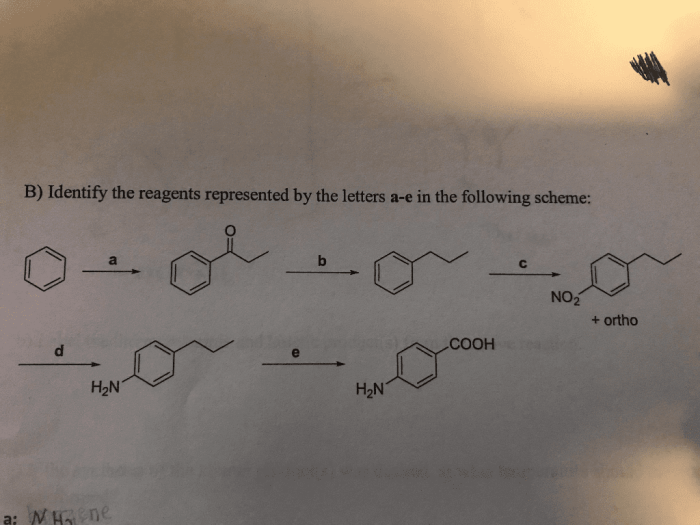
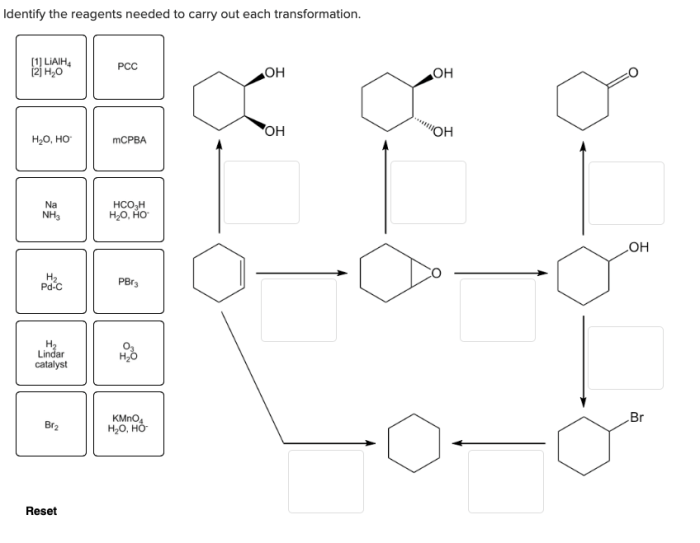
Identify the reagents needed to carry out each reaction. – Delving into the realm of chemical reactions, the identification of reagents stands as a pivotal step in orchestrating successful experiments. Reagents, the essential ingredients of chemical transformations, play a crucial role in determining reaction outcomes and guiding the course of scientific investigations.
This comprehensive guide will illuminate the significance of reagent identification, explore diverse methods for their determination, and provide practical considerations for selecting the most suitable reagents for each reaction.
Unveiling the intricacies of reagent identification, we embark on a journey through various techniques, from scrutinizing physical properties to employing chemical tests and harnessing the power of spectroscopic methods. Each approach offers unique advantages and limitations, empowering researchers with a diverse toolkit for reagent characterization.
Understanding these methods is paramount in ensuring accurate identification and laying the foundation for successful chemical reactions.
1. Identifying Reagents for Chemical Reactions
Identifying reagents is crucial in chemical reactions as they determine the reaction outcome. Reagents are substances that undergo chemical transformations, and their properties dictate the reaction’s course and product formation.
Importance of Reagent Identification
- Predicting reaction products
- Optimizing reaction conditions
- Understanding reaction mechanisms
- Ensuring safety and avoiding hazardous reactions
Examples of Reactions where Reagent Identification is Crucial
- Acid-base reactions: Identifying the strength of acids and bases is essential to predict the reaction outcome and pH changes.
- Redox reactions: Determining the oxidizing and reducing agents is vital to understand electron transfer and predict product formation.
- Organic synthesis: Identifying specific reagents for functional group transformations is crucial for targeted molecule synthesis.
2. Methods for Identifying Reagents
Physical Properties
Observing physical properties like color, odor, and solubility can provide clues about the identity of reagents. For example, a colorless, odorless gas is likely carbon dioxide.
Chemical Tests
- Titration:Measuring the volume of a known reagent required to react with an unknown reagent helps determine its concentration and identity.
- Precipitation:Adding a reagent that forms an insoluble precipitate with the unknown reagent can help identify it.
Spectroscopic Techniques, Identify the reagents needed to carry out each reaction.
- Infrared (IR) spectroscopy:Analyzing the absorption of IR radiation by a reagent can reveal its functional groups.
- Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy:Measuring the nuclear magnetic resonance of atoms within a reagent can provide structural information.
3. Considerations for Reagent Selection
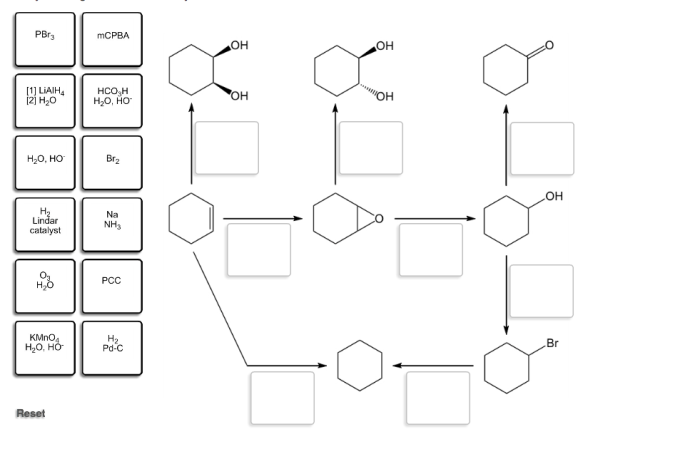
Selecting appropriate reagents is crucial for efficient reactions. Factors to consider include:
Reactivity
The reactivity of reagents affects the reaction rate and product yield. Choosing highly reactive reagents ensures faster reactions.
Cost
Reagent cost can impact the overall cost of a reaction. Selecting cost-effective reagents is important for large-scale or industrial applications.
Availability
Reagents should be readily available or easily synthesized. Scarce or difficult-to-obtain reagents may limit reaction feasibility.
Safety
Safety should be a top priority when selecting reagents. Toxic or hazardous reagents require special handling and disposal procedures.
FAQ Overview: Identify The Reagents Needed To Carry Out Each Reaction.
What is the significance of reagent identification in chemical reactions?
Reagent identification is crucial as it enables researchers to determine the reactants, their stoichiometric ratios, and their properties, which are essential for predicting reaction outcomes, optimizing reaction conditions, and ensuring safety.
How can physical properties aid in reagent identification?
Physical properties such as color, odor, solubility, and melting/boiling points provide valuable clues about the identity of a reagent. By comparing these properties with known values, researchers can narrow down the possibilities and make informed identifications.
What are the advantages of using spectroscopic techniques for reagent identification?
Spectroscopic techniques, such as IR and NMR spectroscopy, offer highly specific and sensitive methods for reagent identification. They provide detailed information about the molecular structure and composition of a reagent, allowing for unambiguous identification.