Welcome to the world of chemistry, where lab 2 separation of a mixture chemistry 1 answers holds the key to understanding the intricate art of separating different components within a mixture. Embark on an enlightening journey as we delve into the techniques, equipment, procedures, and applications of this fundamental concept, unraveling the mysteries of chemistry one step at a time.
As we progress through this guide, you’ll discover the diverse separation techniques employed by chemists, each with its unique advantages and drawbacks. We’ll explore the essential lab equipment used in these experiments, deciphering their functions and applications. Furthermore, we’ll provide a step-by-step walkthrough of the experimental procedure, ensuring your safety and accuracy throughout the process.
Separation Techniques
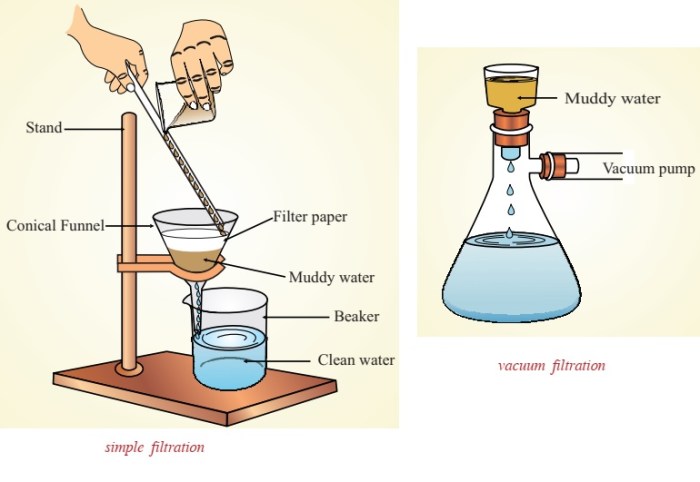
Separation techniques are used in chemistry to separate mixtures into their individual components. There are a variety of separation techniques, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
Filtration
- Filtration is a process of separating solids from liquids or gases by passing the mixture through a filter.
- The filter allows the liquid or gas to pass through, but traps the solids.
- Filtration is a simple and effective way to separate solids from liquids or gases.
Distillation
- Distillation is a process of separating liquids from each other based on their different boiling points.
- The mixture is heated, and the liquid with the lower boiling point vaporizes first.
- The vapor is then condensed and collected.
- Distillation is a very effective way to separate liquids with different boiling points.
Chromatography
- Chromatography is a process of separating mixtures by passing them through a stationary phase.
- The different components of the mixture travel through the stationary phase at different rates, and are thus separated.
- Chromatography is a very versatile technique that can be used to separate a wide variety of mixtures.
Lab Equipment
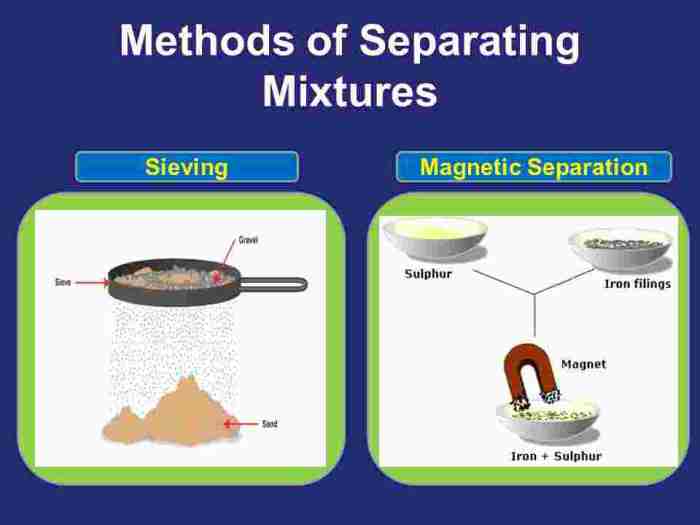
The following lab equipment is used in the separation of mixtures experiment:
Funnel
A funnel is a conical-shaped vessel with a spout at the bottom.
It is used to pour liquids or solids into a container.
Filter paper
Filter paper is a porous paper that is used to filter liquids or gases.
It allows the liquid or gas to pass through, but traps the solids.
Beaker
A beaker is a cylindrical-shaped container with a spout.
It is used to hold liquids or solids.
Test tube
A test tube is a small, cylindrical-shaped container with a rounded bottom.
It is used to hold small amounts of liquids or solids.
Graduated cylinder
A graduated cylinder is a cylindrical-shaped container with a spout and a scale.
It is used to measure the volume of liquids.
Experimental Procedure: Lab 2 Separation Of A Mixture Chemistry 1 Answers
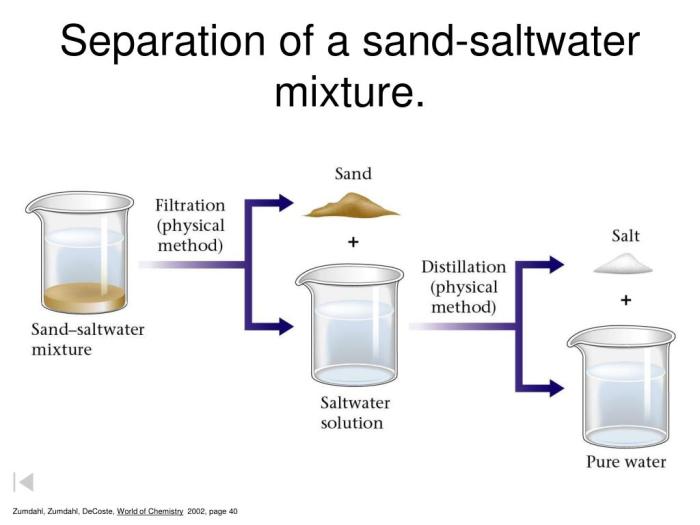
The following steps are involved in the separation of mixtures experiment:
Step 1: Preparation
- Gather the necessary materials.
- Set up the filtration apparatus.
Step 2: Filtration
- Pour the mixture into the funnel.
- Allow the liquid to filter through the filter paper.
- Collect the filtrate in a beaker.
Step 3: Distillation
- Pour the filtrate into a distillation flask.
- Heat the distillation flask until the liquid boils.
- Collect the distillate in a condenser.
Step 4: Chromatography
- Prepare a chromatography column.
- Apply the mixture to the chromatography column.
- Elute the mixture with a solvent.
- Collect the different components of the mixture as they elute from the column.
Data Analysis
The data collected from the separation of mixtures experiment can be used to calculate the following:
Percentage yield
- The percentage yield is the amount of product obtained divided by the amount of product that was theoretically possible to obtain.
- The percentage yield is expressed as a percentage.
Purity
- The purity of a product is the amount of product that is free of impurities.
- The purity of a product is expressed as a percentage.
Efficiency
- The efficiency of a separation technique is the amount of product that is obtained divided by the amount of product that was present in the original mixture.
- The efficiency of a separation technique is expressed as a percentage.
Applications
Separation techniques are used in a wide variety of applications, including:
Chemical industry
- Separation techniques are used to separate the different components of petroleum.
- Separation techniques are used to produce chemicals such as plastics and pharmaceuticals.
Food industry
- Separation techniques are used to separate the different components of milk.
- Separation techniques are used to produce food products such as cheese and yogurt.
Environmental industry, Lab 2 separation of a mixture chemistry 1 answers
- Separation techniques are used to separate pollutants from water and air.
- Separation techniques are used to recycle materials such as paper and plastic.
FAQs
What is the purpose of lab 2 separation of a mixture chemistry 1?
Lab 2 separation of a mixture chemistry 1 aims to provide students with hands-on experience in separating different components within a mixture using various techniques, fostering a deeper understanding of their properties and behaviors.
What are the different separation techniques covered in this lab?
This lab covers a range of separation techniques, including filtration, distillation, extraction, and chromatography, each tailored to specific types of mixtures and separation requirements.
How is the experimental data analyzed in this lab?
Data analysis involves calculating yields, interpreting graphs, and drawing conclusions based on the observed results, allowing students to assess the efficiency and accuracy of the separation techniques employed.