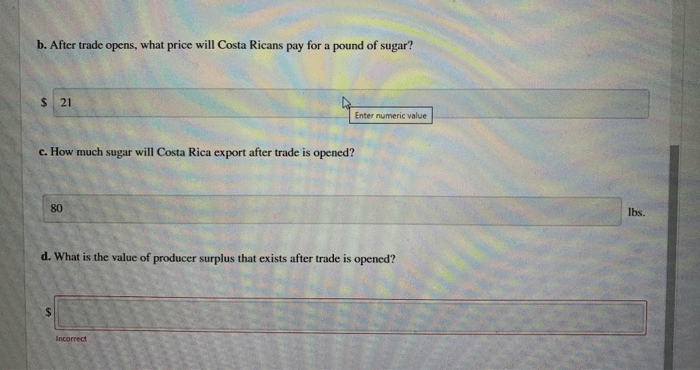
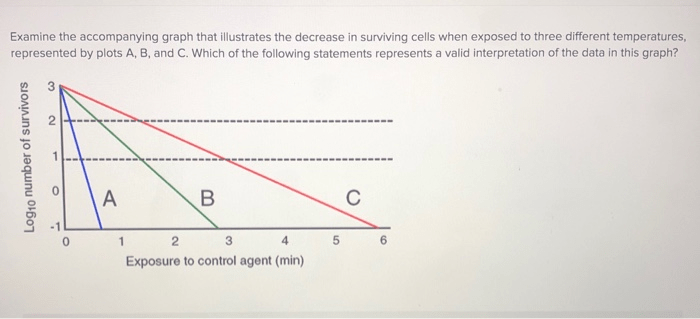
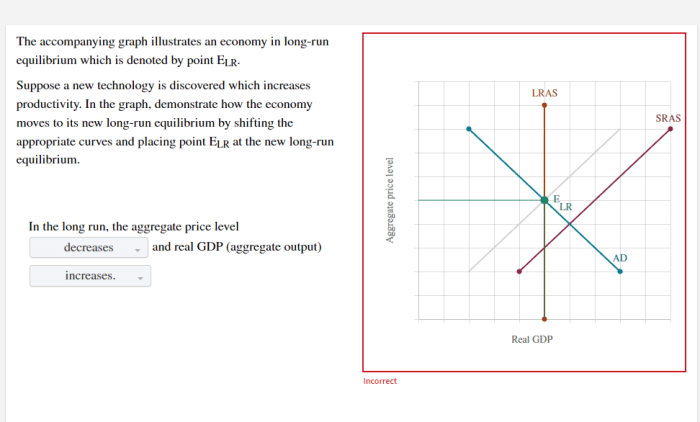
The accompanying graph illustrates a market for cigarettes – With the accompanying graph illustrating a market for cigarettes, this discourse embarks on an exploration of the dynamics that shape this industry. By examining market structure, demand and supply, elasticity, government intervention, and external factors, we unravel the complexities that determine the equilibrium price and quantity, as well as the potential consequences of various interventions.
This in-depth analysis provides insights into the forces that influence market outcomes, offering valuable knowledge for policymakers, industry stakeholders, and anyone seeking to understand the intricacies of cigarette markets.
Market Structure
Market structure refers to the number and size distribution of buyers and sellers in a market. It influences market behavior, pricing, and competition. The graph illustrates a market with a large number of buyers and sellers, each having a negligible impact on the market price.
This is known as a perfectly competitive market.
Characteristics of Perfect Competition:, The accompanying graph illustrates a market for cigarettes
- Many buyers and sellers
- Homogeneous products
- Free entry and exit
- Perfect information
Demand and Supply
| Price | Quantity Supplied | Quantity Demanded | Market Surplus/Shortage |
|---|---|---|---|
| $10 | 100 | 150 | -50 (Shortage) |
| $15 | 120 | 130 | -10 (Shortage) |
| $20 | 140 | 110 | 30 (Surplus) |
| $25 | 160 | 90 | 70 (Surplus) |
The law of demand states that as price increases, quantity demanded decreases. The law of supply states that as price increases, quantity supplied increases. The equilibrium point is where quantity supplied equals quantity demanded, which is at a price of $20 and a quantity of 110.
Elasticity
Price elasticity of demand measures the responsiveness of quantity demanded to changes in price. In this market, the elasticity of demand is -0.5, which indicates that a 1% increase in price leads to a 0.5% decrease in quantity demanded. Price elasticity of supply measures the responsiveness of quantity supplied to changes in price.
In this market, the elasticity of supply is 0.6, which indicates that a 1% increase in price leads to a 0.6% increase in quantity supplied.
Elasticity is important in this market because it determines the slope of the demand and supply curves. A more elastic demand curve means that a change in price will have a smaller impact on quantity demanded. A more elastic supply curve means that a change in price will have a smaller impact on quantity supplied.
Government Intervention
Governments may intervene in markets to address market failures or achieve policy objectives. In the cigarette market, potential government interventions include:
- Price ceilings: A maximum price set below the equilibrium price, which can lead to shortages.
- Price floors: A minimum price set above the equilibrium price, which can lead to surpluses.
Government intervention can impact market equilibrium by shifting the demand or supply curves. This can lead to changes in price, quantity, and market surplus/shortage.
External Factors: The Accompanying Graph Illustrates A Market For Cigarettes
External factors can also affect the market for cigarettes. These include:
- Changes in income: Higher incomes can lead to increased demand for cigarettes.
- Changes in population: A growing population can lead to increased demand for cigarettes.
- Changes in health concerns: Increased awareness of the health risks associated with smoking can lead to decreased demand for cigarettes.
External factors can impact market equilibrium by shifting the demand or supply curves. This can lead to changes in price, quantity, and market surplus/shortage.
Detailed FAQs
What is the equilibrium price in a cigarette market?
The equilibrium price is the price at which the quantity supplied equals the quantity demanded, resulting in market equilibrium.
How does government intervention affect the cigarette market?
Government interventions, such as price ceilings and floors, can disrupt market equilibrium, leading to surpluses or shortages and potentially unintended consequences.
What external factors can influence the demand for cigarettes?
External factors such as changes in income, population, and health concerns can impact the demand for cigarettes, shifting the demand curve and affecting market outcomes.