The homologous analogous and vestigial structures worksheet embarks on an enlightening journey into the captivating realm of comparative anatomy, where we delve into the fascinating similarities and differences among living organisms. This comprehensive guide unveils the intricate connections between structure, function, and evolutionary history, providing a deeper understanding of the remarkable diversity of life on Earth.
Through a meticulous examination of homologous, analogous, and vestigial structures, we uncover the profound influence of natural selection on the evolution of species. These structures serve as compelling evidence for the interconnectedness of all living things, showcasing the remarkable tapestry of life’s intricate adaptations.
Homologous Structures
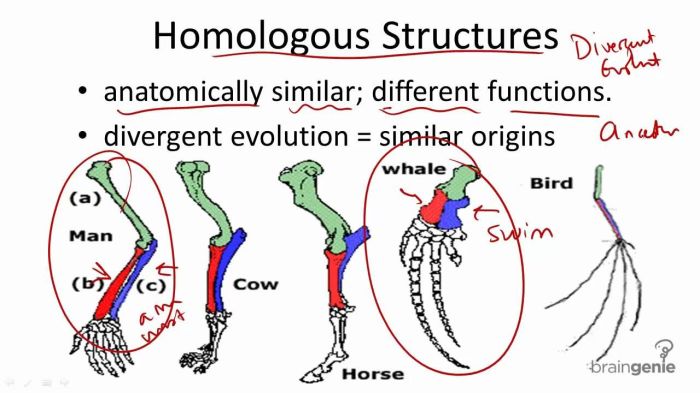
Homologous structures are anatomical features that share a common evolutionary origin, despite serving different functions in different species. These structures provide evidence of the shared ancestry of different organisms.
Examples:
- The forelimbs of humans, bats, and whales have the same basic bone structure, despite their different functions (walking, flying, and swimming).
- The petals of a flower are homologous to the leaves of a plant, both arising from the same embryonic tissue.
Evolutionary Significance:
Homologous structures support the theory of evolution by demonstrating the common ancestry of different species. They suggest that these species have evolved from a common ancestor that possessed these structures, which were then modified over time to adapt to different environments.
Analogous Structures, Homologous analogous and vestigial structures worksheet
Analogous structures are anatomical features that serve similar functions in different species, but do not share a common evolutionary origin. These structures arise independently in response to similar environmental pressures.
Examples:
- The wings of birds and bats are analogous structures, both adapted for flight, but with different skeletal structures.
- The eyes of humans and octopuses are analogous structures, both adapted for vision, but with different structural components.
Adaptive Significance:
Analogous structures demonstrate the power of natural selection to independently evolve similar solutions to similar environmental challenges. They provide evidence for convergent evolution, where different species adapt to similar environments by developing similar traits.
Vestigial Structures
Vestigial structures are anatomical features that have lost their original function in a particular species but are still present in a reduced or rudimentary form. They are remnants of structures that were once functional in an ancestor.
Examples:
- The human tailbone (coccyx) is a vestigial structure that is a remnant of a tail in our evolutionary ancestors.
- The wisdom teeth in humans are vestigial structures that are no longer necessary for chewing and are often removed.
Evolutionary History and Function:
Vestigial structures provide evidence for the evolutionary history of a species. They suggest that these structures were once functional but have become redundant over time as the species has adapted to new environments or changed its lifestyle.
Evidence for Evolution:
The presence of vestigial structures is a strong argument for evolution. It demonstrates that organisms have changed over time and that some structures have become unnecessary as the environment and lifestyle of a species have changed.
Worksheet Analysis
Exercises and Questions:
- Identify homologous structures in different organisms and explain their evolutionary significance.
- Compare and contrast analogous and homologous structures, providing examples from different species.
- Analyze the evidence for vestigial structures as proof of evolution, citing specific examples.
Table or Bulleted List:
| Structure Type | Examples | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Homologous | Forelimbs of humans, bats, and whales | Share a common evolutionary origin, despite different functions |
| Analogous | Wings of birds and bats | Serve similar functions, but do not share a common evolutionary origin |
| Vestigial | Human tailbone | Remnants of structures that were once functional in ancestors |
FAQ Compilation: Homologous Analogous And Vestigial Structures Worksheet
What are homologous structures?
Homologous structures are anatomical features that share a common evolutionary origin despite serving different functions in different species.
How do analogous structures differ from homologous structures?
Analogous structures serve similar functions but lack a common evolutionary origin, arising independently in different lineages due to convergent evolution.
What is the significance of vestigial structures?
Vestigial structures are remnants of ancestral structures that have lost their original function over time, providing evidence for evolutionary change.